CT Scan for Lung Cancer Screening: A Comprehensive Guide
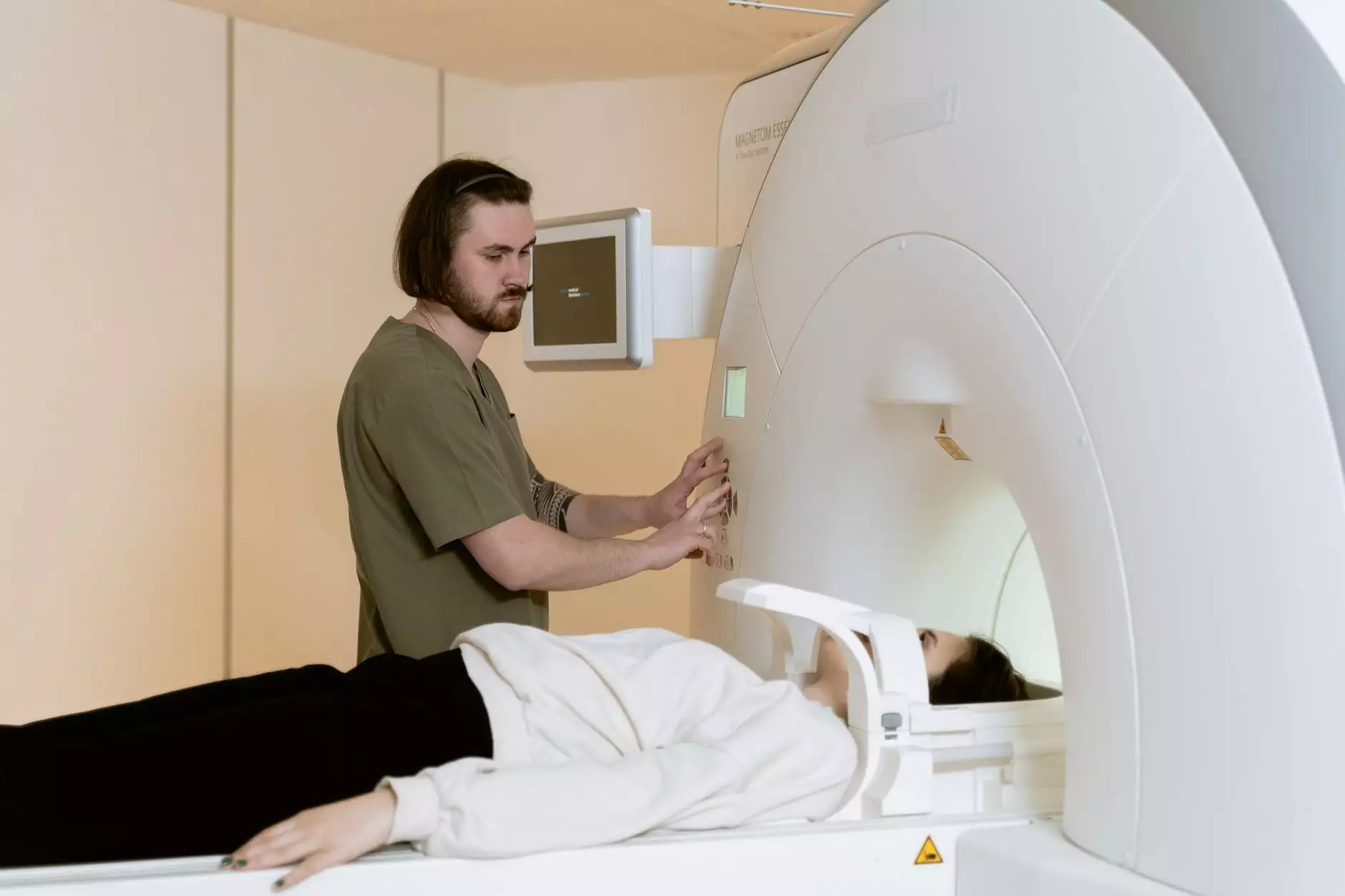
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a significant health challenge worldwide, being one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. The two main types of lung cancer are:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
Early detection is crucial for improving survival rates, making screening methods like CT scan for lung cancer screening vital for those at risk.
What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan combines multiple X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside your body. It provides more detailed information than regular X-rays, enabling radiologists to identify abnormalities effectively.
Importance of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Screening
The role of CT scans in lung cancer screening cannot be overstated. They are particularly recommended for high-risk individuals, such as long-term smokers, former smokers, and those with a family history of lung cancer.
Benefits of CT Scans
- Early Detection: Early detection of lung cancer significantly enhances treatment options and survival rates.
- High Sensitivity: CT scans can detect small nodules or tumors that may be missed by standard X-rays.
- Non-invasive Procedure: A CT scan is a painless, convenient way to get an in-depth look at lung health.
Who Should Consider a CT Scan for Lung Cancer Screening?
Screening with CT scan for lung cancer is particularly recommended for:
- Individuals aged 55 to 80 years.
- Current smokers or those who have quit within the last 15 years.
- Individuals who have a smoking history of at least 30 pack-years (a pack-year is defined as smoking one pack of cigarettes a day for one year).
- People with a family history of lung cancer or specific genetic markers.
The Screening Process
Preparation
Before the CT scan, patients will receive detailed instructions from their healthcare provider, which may include:
- Information on whether to eat or drink before the scan.
- Advice on removing jewelry or clothing that could interfere with the imaging.
- Guidance about any medications or supplements to avoid.
During the Scan
During the CT scan, patients lie on a movable table while a rotating machine takes images of the lungs. The process typically lasts 10 to 30 minutes, and patients may be asked to hold their breath briefly while the images are captured.
After the Scan
After the procedure, patients can usually resume their normal activities immediately. A radiologist will analyze the scans, and results are typically available within a few days.
Understanding the Results
CT scan results can vary widely. Radiologists look for:
- Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: Small, round growths in the lung that may require further testing.
- Masses: Larger growths that could indicate cancer.
- Infiltrates: Areas of increased density that may suggest infection or inflammation.
If abnormalities are detected, further testing such as a biopsy may be recommended to determine if cancer is present.
Risks and Considerations
While CT scans are generally safe, they do expose patients to a small amount of radiation. The benefits, particularly in high-risk populations, typically outweigh the potential risks. Doctors make individualized recommendations to weigh the risks and benefits of CT scans for lung cancer screening.
Current Guidelines for Lung Cancer Screening
Guidelines for lung cancer screening have been established by organizations such as:
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF)
- American Cancer Society (ACS)
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN)
These guidelines help healthcare providers identify high-risk individuals who would benefit from screening and ultimately lead to earlier detection and better outcomes.
Advancements in Screening Technology
The field of medical imaging is constantly evolving. New advancements in CT technology enhance the screening process:
- Low-Dose CT Scanning: Innovations now allow for lower radiation doses while maintaining image clarity.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are being developed to assist radiologists in identifying suspicious nodules more accurately.
- 3D Imaging: Provides radiologists with a more comprehensive view of lung structures.
Conclusion: The Future of Lung Cancer Screening
As the medical community continues to research and develop new technologies, the future of lung cancer screening looks promising. The role of the CT scan for lung cancer screening remains instrumental in early detection, enabling timely intervention and improving patient outcomes.
At Neumark Surgery, we are committed to staying at the forefront of lung cancer screening and treatment. Our dedicated team of professionals is here to ensure you receive the highest standard of care throughout your screening journey.
© 2023 Neumark Surgery. All Rights Reserved.